If you are unsure of the different postgraduate courses available, this page will help. We will cover the main types of master’s degrees available in the UK. Once you know the best programme for you, you can search postgraduate courses by certificate type on our dedicated master’s page.
The postgraduate degree you take depends on your future goals and ambitions. In fact, when looking at different courses, think about what your end destination is and work backwards to find the right study options that will help you get there. Use the overview below to understand the certificate titles and the difference between professional master’s degrees and research master’s degrees.
Research Master’s Degree
Research Masters’ degrees (MRes) are more focused on independent work. They are usually used as a stepping stone towards are PhD or a career as a researcher.
On an MRes, around 70% of the work is independent research. These courses tend to have a more significant dissertation or practice lead research project. There are no taught modules, but there is often training on research methods and ethics and writing research and funding proposals.
Another type of research master’s degree is called a Master of Philosophy. This is not a master’s in philosophy but a research master usually lasting two years consisting of a single major piece of research. Candidates who take an MPhil tend to build on this work to complete a PhD, an even more advanced research-based degree.
Taught Master’s Degrees
Taught master s degrees are made up of taught courses or modules led by a tutor or programme leader. Students typically attend weekly lectures and seminars. Students progress through the structured course modules building up to a final project.
The final project or dissertation often accounts for the final third of the course. This work is similar to the investigation that happens on a research degree. There is a wide variety of taught master’s programmes, and some have a more substantial research component than others.
It is possible to use a taught master’s to progress to a PhD, but most use the specialist knowledge gained in this type of master’s degree program to develop their professional practice and career development.
Masters Conversion Courses
These taught master’s degrees are designed for students who already have an undergraduate degree in an unrelated subject to their career goals. A master’s conversion course is a way to gain entry to specific professions or make a career change. Law, psychology and teaching are popular choices.
For example, if you graduated with a bachelor’s degree in English and after three years of working in an unrelated job you wanted to become a teacher, then a PGCE (Postgraduate Certificate in Education ) would be the ideal conversion course to take.
These postgraduate courses are intense and vocational focussed. Some careers require a postgraduate diploma or certificate for entry-level positions, like the teaching example above. In contrast, others require a complete master’s degree, such as Law.
Popular Postgraduate conversion courses
- Journalism MA
- Law Conversion LLM
- Social Work MSc
- Psychology MSc
- Postgraduate Certificate in Education PGCE
Integrated Master’s Degrees
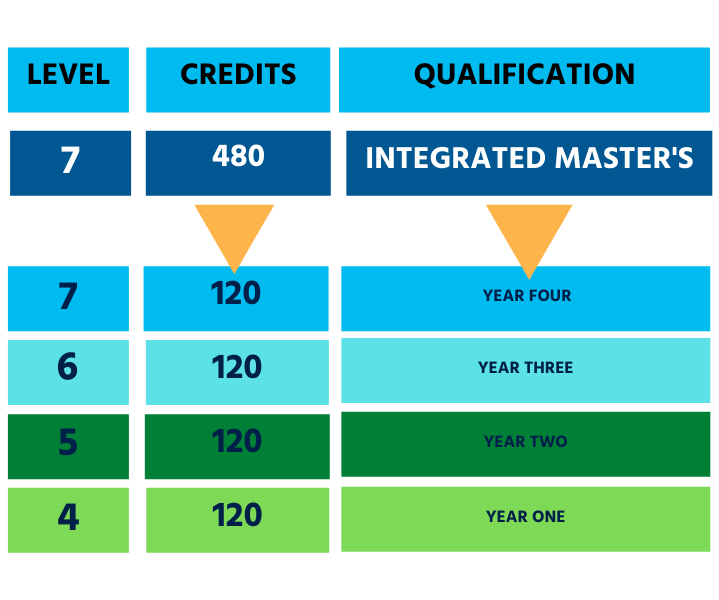
An integrated master’s degree combines undergraduate and postgraduate study in one course. You study 480 credits made up of 360 credits at levels 4, 5, and 6, followed by at least 120 credits at level 7. This is slightly less than the 180 credits at level 7 on a stand-alone master’s degree.
Most universities provide only one final certificate for an integrated master’s, but some award a degree and masters. On an integrated master’s, you typically have a choice after two years to continue on the master’s path or move to a three-year undergraduate degree. At some universities, you must achieve a specified grade at the end of two years to progress on the master’s pathway.
Master’s Degrees That Are Not Master’s Level
Finally, some master’s degrees are not at master’s level or even academic qualifications. The ancient universities of Cambridge, Oxford and Dublin provide master’s degrees awarded without any examination. Students who have held a bachelor of Art (BA) for a set number of years are eligible to request an MA. Granting a master’s in this way has been controversial in the past, but they remain to this day.
Types Of Master’s Degrees Certificates Explained
Master of Art- MA
A Master of Arts is not only attributed to art courses. This master’s type can be awarded for business, marketing, and social sciences subjects.
Master of Science- MSc
A master of sciences, as the name suggests, has a focus on the sciences and research. An MSc can indicate that a course has a quantitative component even though it is a social science. For example, a Psychology MSc will likely involve more statistics than a psychology MA.
Master of Business Administration- MBA
An MBA degree is an intense conversion course covering many business functions designed for business leaders and managers.
Master of Public Administration (MPA)
An MPA is designed for managers in the public sector. These courses are designed to understand and address the challenges in public and not for profit sectors.
Master of Laws- LLM
An LLM is a conversion course that opens up a career in the legal profession for graduates with a non-related bachelor’s degree.
Master of Engineering- MEng
An MEng is a specialist engineering degree that can either be research-focused or a professional master’s degree.
Master of Public Health- MPH
An MPH is a multidisciplinary postgraduate master’s degree that looks at how to improve the health of entire populations.
Master’s Degree Certificate FAQ
What is the difference between an MA and an MSc?
A Master of Art (MA) focuses on the arts, while a Master of Science (MSc) is involved in the sciences. For example, Psychology MSc science degrees would have more statistics and quantitative work than psychology MA arts degrees.
Is an MBA a higher level than other masters?
No, an MBA is a level 7 qualification like all other master’s degrees. However, an MBA is seen as a highly desirable qualification by businesses. As such, MBA graduates can see a significant increase in their salaries and career progression.
If I complete a master can I get PgCert and PgDip certificates as well?
No, you cannot get three certificates for one course. However, on many programmes, you can stop studying at specific points in the course and leave with a certificate or diploma or continue studying for the complete master’s qualification.
How many types of Masters are there?
All master’s degrees in the UK can be split into two main types. Taught and Research. However, the QA characterises taught masters into two groups-
- Professional or practice master’s degrees
- Specialised or advanced study master’s degrees
The terms used by the QA are more commonly used among university teams and course designers. When looking at courses, you will most likely come across the terms research Taught and Conversion Masters Degrees.